Printing Technologies
Our printing facilities can be divided into two topics; structural printing using commercial 3D printers and functional printing using a commercial laboratory printer. The structural printers are used to create components for our scientific setups, while in functional printing the structures created have unique new features.
Structural Printing
- 1 Fused deposition machine with the following features:
- Layer resolution: > 50 µm
- can handle: PLA, ABS, PC, Nylon
- 3 Stereolithography machines with the following features:
- Various materials available
- Resolution down to 25 µm
 |
 |
|
| The Roland ARM 10 as an example for the stereolithography printers. | The Ultramaker 2+ fused deposition modeler. |
Functional Printing
In our research, we focus on using inkjet printing based on a FujiFilm Dimatix printer to achieve new functionality mainly in the area of magnetic resonance imaging. The following examples show the versatility of the technology.
 |
 |
 |
||
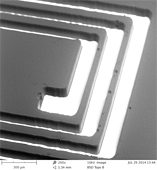
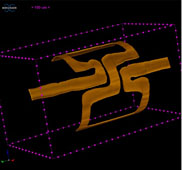
| The bottom of the trenches are covered with inkjetted silver tracks, which were also used as shadow masks to create the trenches. | A µCT image of an inkjet printed rolled up MRI coil. | Under the Kiwi is a planar MRI coil that was inkjekt printed on Kapton foil. The MR image can be seen in the inset. |
The printers can be used for various materials and chemicals that have particles belows 1 µm and can be modified to a viscosity of ~10 mPas.

