Solar domestic heat pump technologies in Germany
- Type:Master Thesis
- Supervisor:
- Field of Study:
Mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, physics and related programs of study
Job's Description:
We are looking for ambitious, creative and self-motivated individuals, who like to work in a multidisciplinary and international team.
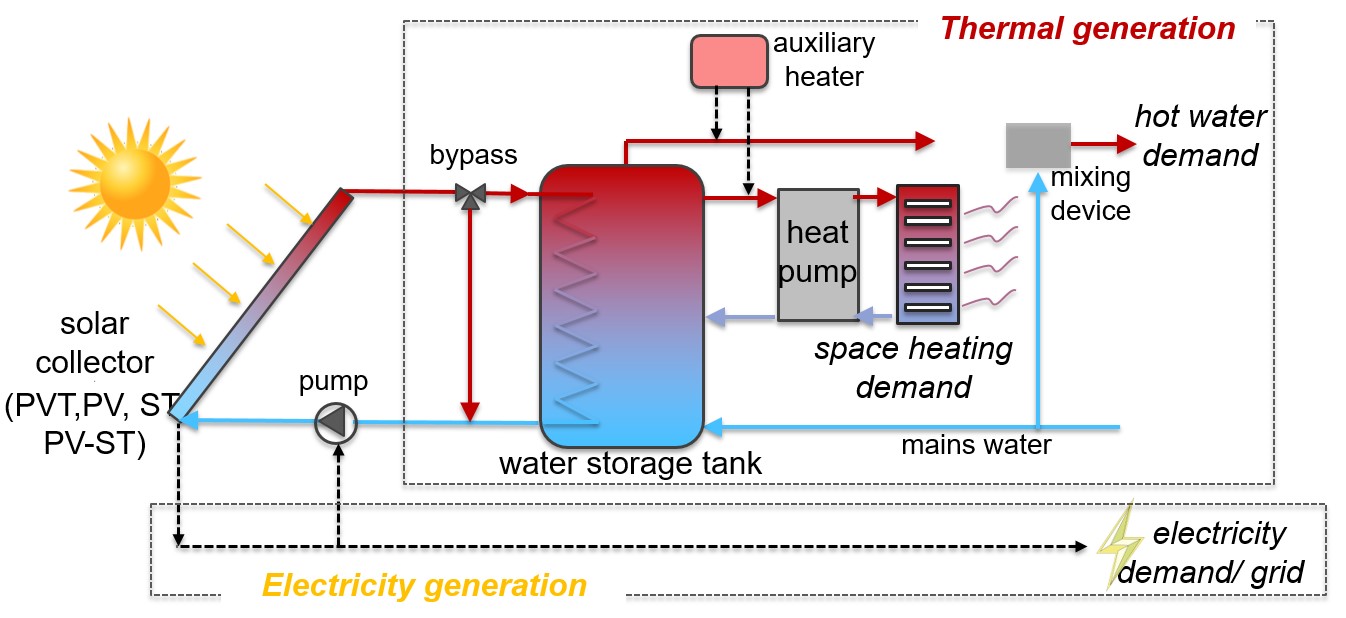
Major economies are adopting laws to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. Meeting the increasing demand for heat and the associated wide-ranging and diverse challenges requires exploiting energy resources in the most efficient, cost-effective and sustainable way possible. Novel systems to improve the fuel-to-heat efficiency in domestic heating applications are required. In this thesis, a techno-economic comparative study is conducted to assess the competitiveness of four technologies for domestic heating in Germany: (i) electricity-driven standalone heat pumps; (ii) electricity-driven solar-assisted heat pumps; (iii) hydrogen-driven absorption heat pumps; and (iv) conventional natural gas boilers, for different scenarios.
The overall aim of the research is to present a methodology for identifying promising heat pump technologies that can be used to meet the demand for space heating and hot water in domestic applications. The trade-offs between the cost and performance of different current and disruptive heat-pump solutions will be explored and the techno-economic potential of innovative systems will be assessed and compared against conventional natural gas-fired heating technologies. The objectives of the thesis are:
- To compare heat pump solutions in terms of payback time, total lifetime cost, levelized cost of energy, total cost, consumed electricity power and environmental impact
- To compare heat pump solutions under different fuel prices, i.e., electricity, natural gas and hydrogen prices
- To compare heat pump solutions under different price-reduction predictions for solar panels, absorption heat pumps and electricity-driven heat pumps
- To compare heat pump solutions under different economic parameters, i.e., market discount rate and fuel inflation rate
- To explore potential incentives (e.g., subsidies, grants) that can lead towards optimal technology uptake and heat decarbonisation
Required resources/skills:
• Interest in thermodynamic analysis and modelling of energy systems and heat pump systems are desirable for this project. Basic models will be provided, and the student will need to understand and develop them further, performing specific case studies.
• The models will be developed in MATLAB environment hence the student should have some experience with that particular language.
Contract's Duration: 6-8 Months Entry Date: on Appointment
click here for more information and online apply
Fachliche/r Ansprechpartner/in
Dr. Jingyuan Xu
Karlsruher Institut für Technologie
Institut für Mikrostrukturtechnik
Postfach 3640
76021 Karlsruhe
Telefon: +49 721 608-24781
E-Mail: jingyuan.xu∂kit.edu

